In today’s fast-paced world of industrial manufacturing, the transformation brought about by digitization has opened up unprecedented possibilities for efficiency, connectivity, and innovation. Every machine, sensor, and component communicates seamlessly, promising optimized operations and heightened productivity. But lurking beneath the surface lies a formidable adversary that can disrupt the very core of industrial manufacturing: cyber threats.
With the ever-increasing digitization of the industrial sector, unique cybersecurity challenges have emerged, demanding immediate action. The interconnectedness of industrial systems, encompassing legacy infrastructure, Industrial Control Systems (ICS), and Internet of Things (IoT) devices, presents an expansive attack surface for malicious actors. The repercussions of a successful cyberattack are far-reaching, from crippling financial losses and disruptive production downtime to compromised safety and irreparable damage to reputation. Protecting industrial manufacturing from these threats extends beyond safeguarding sensitive information; it ensures the resilience and continuity of critical operations.
While cybersecurity concerns have long plagued other industries, the realm of industrial manufacturing presents its complex challenges. Unlike traditional IT networks, industrial systems possess unique requirements and constraints, necessitating tailored security solutions. Tackling these challenges requires a holistic approach encompassing technological advancements, organizational culture, governance frameworks, and stakeholder collaboration. As cyber threats grow increasingly sophisticated and persistent, industrial manufacturers must adopt a proactive and vigilant stance, embedding robust cybersecurity measures within their digitization strategies.
So, contemplating the rising cyber threats, let’s explore the intricacies of cybersecurity challenges in the era of industrial manufacturing digitization. From uncovering the risks and vulnerabilities manufacturers face to outlining best practices and emerging technologies, we’ll discuss the complexities of securing the digital future of industrial manufacturing and discover the proactive measures that will keep us one step ahead of the constant and looming cyber threats. Ready to read? Let’s Begin!
Introduction to Industrial Manufacturing Digitization
Industrial manufacturing digitization refers to integrating advanced technologies and data-driven systems into the manufacturing processes of various industries. This transformative shift aims to optimize operations, enhance productivity, and increase efficiency in the production ecosystem.
The core principle behind industrial manufacturing digitization is the use of digital technologies to automate and streamline traditional manufacturing processes. This involves adopting robotics, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, Artificial Intelligence (AI), cloud computing, and data analytics. These technologies collect, analyze, and utilize data to drive informed decision-making and process optimization.
Manufacturers gain access to real-time data about their operations through digitization, enabling them to monitor and control various aspects of the production process. This data can be leveraged to identify inefficiencies, optimize workflows, and make predictive maintenance decisions to minimize downtime and improve overall equipment effectiveness.
Additionally, industrial manufacturing digitization offers greater customization and flexibility in production. As a result, manufacturers can adapt their processes to accommodate individual customer needs, optimize supply chain management, and respond quickly to market demands.
Overall, industrial manufacturing digitization represents a paradigm shift in the way manufacturing operations are conducted. It empowers manufacturers to leverage advanced technologies and data-driven insights to drive efficiency, productivity, cost savings, and innovation in an increasingly competitive global marketplace.
But the real question is – Are there any significant benefits of Industrial Manufacturing Digitization? Let’s explore.
The Benefits and Advantages of Digitization
Digitization in industrial manufacturing brings forth a wide range of benefits and advantages that have a transformative impact on the industry. Here is a detailed elaboration of the key benefits and advantages:
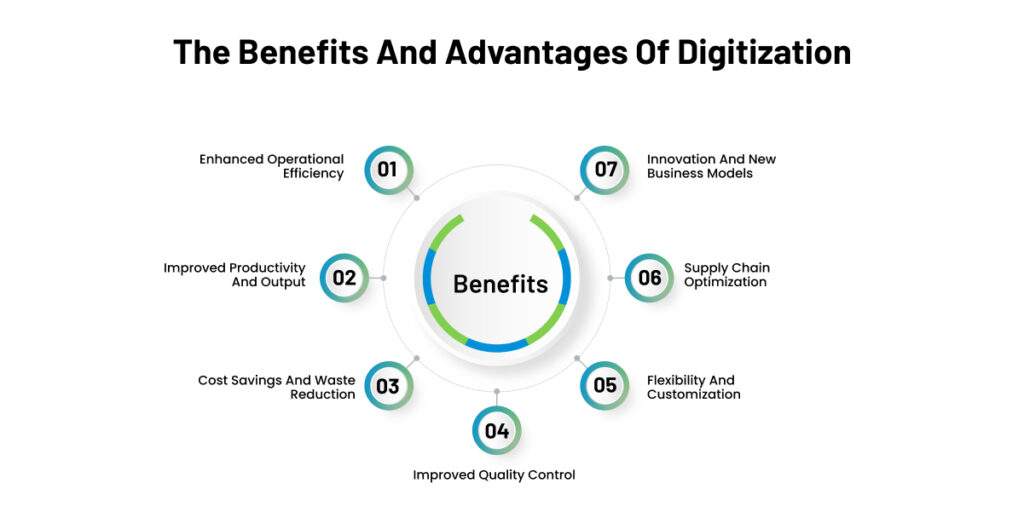
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: Digitization streamlines processes, automates tasks, and optimizes resource allocation, improving operational efficiency in industrial manufacturing.
- Improved Productivity and Output: Digital technologies leverage data analytics and machine learning to identify inefficiencies, optimize machine performance, and boost productivity, increasing output levels.
- Cost Savings and Waste Reduction: Digitization minimizes costs by eliminating manual labor, optimizing operations, and improving inventory management, resulting in significant cost savings and waste reduction.
- Improved Quality Control: Real-time monitoring and data analysis enable early detection of anomalies, ensuring consistent adherence to quality standards and enhancing product quality.
- Flexibility and Customization: Digitization empowers manufacturers to respond quickly to market demands and customize products to meet customer needs, enhancing flexibility and customer satisfaction.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Digitization enables better coordination, visibility, and collaboration throughout the supply chain, optimizing inventory management, reducing lead times, and improving overall efficiency.
- Innovation and New Business Models: Digitization fuels innovation by leveraging advanced technologies and data insights to create smart factories, develop new products and services, and explore innovative business models.
In summary, the benefits and advantages of digitization in industrial manufacturing are far-reaching, transforming the industry and paving the way for improved efficiency, productivity, and innovation. However, it is essential to recognize that with the increasing digitization and interconnectedness of industrial systems, the criticality of cybersecurity cannot be overlooked.
So, moving ahead, let’s further look into the cybersecurity challenges in the digitized industrial manufacturing environment and explore the potential risks and threats that can compromise the integrity, safety, and continuity of operations.
Importance of Cybersecurity in Industrial Manufacturing
The significance of cybersecurity in the digitized industrial manufacturing environment cannot be emphasized enough. As industrial systems become more interconnected, the risks and vulnerabilities associated with cyber threats have reached a critical level. Therefore, it is of utmost importance for manufacturers to prioritize cybersecurity as an essential aspect of their operations. By doing so, they can protect their valuable assets, ensure uninterrupted production processes, safeguard sensitive data, and uphold the safety of their workforce and the environment.
The potential consequences of cyber threats in the industrial manufacturing sector are far-reaching and severe. Here are a few key aspects that underscore the potential impact:

Operational Disruption: Cyberattacks can disrupt industrial operations, targeting critical systems like ICS and SCADA, leading to costly downtime, delays, and equipment failures.
Intellectual Property Compromise: Cyberattacks on manufacturing systems can result in the theft or compromise of valuable intellectual property, such as designs, algorithms, and trade secrets, causing financial setbacks and undermining competitiveness.
Safety and Environmental Risks: Cyberattacks on safety systems can endanger employees and the environment, manipulating controls and parameters that may lead to accidents, equipment malfunctions, or environmental disasters.
Supply Chain Disruptions: Cyberattacks on suppliers or logistics partners can disrupt the entire supply chain, causing delays, shortages, and financial losses, with ripple effects impacting multiple stakeholders.
Financial and Reputational Damage: Successful cyberattacks result in financial implications, legal fees, penalties, and damage to the manufacturer’s reputation, leading to loss of business opportunities, decreased market share, and long-term brand damage.
The industrial manufacturing sector has become an attractive target for cybercriminals due to its potential impact and monetary gains. The increasing frequency of cyberattacks targeting industrial systems underscores the criticality of implementing robust cybersecurity measures. Manufacturers must adopt a proactive approach, leveraging technologies such as network segmentation, encryption, intrusion detection and prevention systems, continuous monitoring, and comprehensive employee training to mitigate the evolving risks posed by cyber threats.
Further, let’s delve deeper into the cybersecurity challenges of digitized industrial manufacturing. Additionally, we will discuss proactive measures and strategies necessary to secure these systems and effectively combat the evolving landscape of cyber threats.
Also, Read – Revolutionary Manufacturing Industry Solutions: The Digital Manufacturing Approach
Cybersecurity Challenges in Industrial Manufacturing
Industrial manufacturers encounter numerous cybersecurity challenges in their pursuit of securing their operations. Here, we delve into the specific complexities and risks faced in terms of cybersecurity in the industrial manufacturing sector:
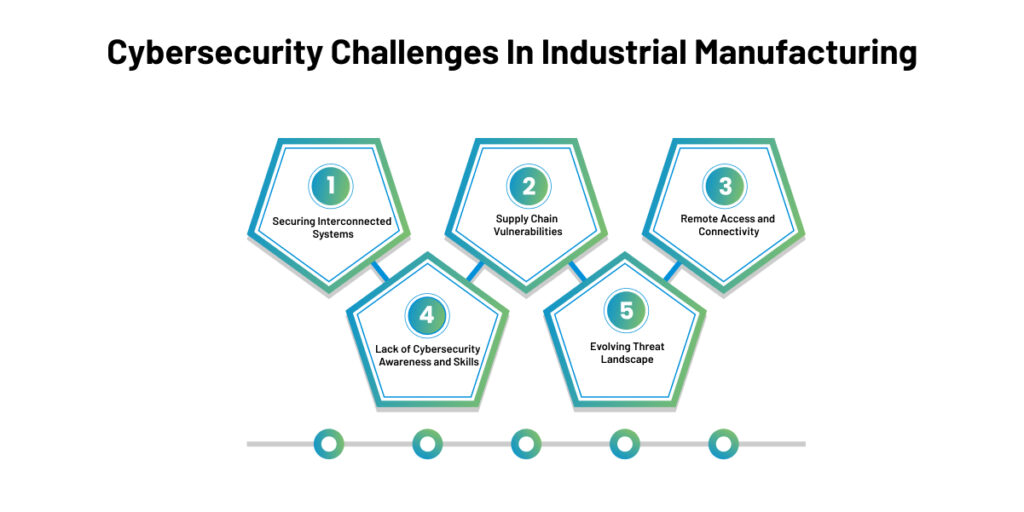
Securing Interconnected Systems
- Legacy Infrastructure: Many industrial manufacturers have legacy systems not originally designed with cybersecurity in mind. These outdated systems may lack robust security features, making them vulnerable to cyber threats.
- Industrial Control Systems (ICS) and SCADA Systems: These critical systems control and monitor industrial processes. Protecting them is crucial, as any compromise could lead to operational disruptions, equipment damage, or safety hazards.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Devices: The proliferation of IoT devices in industrial environments introduces new attack surfaces. If not properly secured, cybercriminals can exploit these devices to gain unauthorized access to the network or compromise critical systems.
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
- Third-Party Integrations: Industrial manufacturers often rely on third-party vendors and suppliers. Integrating external systems and components into their infrastructure increases the risk of cyber threats, as these systems may introduce vulnerabilities or be compromised.
- Supply Chain Attacks: Adversaries may target the supply chain to gain unauthorized access to industrial systems. This can involve tampering with components or software during manufacturing or distribution, leading to potential backdoors or malware infections.
Remote Access and Connectivity
- Remote Access to Industrial Systems: Remote access is often necessary for maintenance, updates, and troubleshooting. However, if not adequately secured, remote access can become an entry point for cyberattacks, allowing unauthorized individuals to infiltrate and compromise industrial systems.
- Increased Connectivity: The convergence of operational technology (OT) and information technology (IT) systems brings enhanced connectivity and increases the attack surface. Connectivity introduces potential vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit to gain unauthorized access or disrupt operations.
Lack of Cybersecurity Awareness and Skills
- Workforce Education: Industrial manufacturers may face challenges in cultivating a cybersecurity-aware culture among their workforce. Lack of cybersecurity knowledge and training can lead to unintentional mistakes or risky behaviors that expose systems to cyber threats.
- Shortage of Cybersecurity Professionals: The demand for skilled cybersecurity professionals exceeds the available talent pool. Industrial manufacturers may struggle to recruit and retain qualified personnel to implement and manage cybersecurity measures effectively.
Evolving Threat Landscape
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): Industrial manufacturers are increasingly targeted by sophisticated APT groups seeking continued access to their systems and data. These well-funded adversaries employ advanced techniques, such as social engineering, zero-day exploits, and tailored malware, to bypass traditional security measures.
- Ransomware Attacks: Ransomware has emerged as a significant threat to industrial manufacturers. These malicious attacks can encrypt critical systems and data, disrupting operations and demanding ransom payments in exchange for decryption keys. The financial and operational impact of successful ransomware attacks can be severe.
- Insider Threats: The insider threat, whether intentional or accidental, poses significant risks to industrial cybersecurity. Employees or contractors with privileged access to systems may intentionally misuse their privileges or inadvertently introduce vulnerabilities through negligent actions, such as clicking on malicious links or sharing sensitive information.
The escalating cyber threats industrial manufacturers face in the era of digitized manufacturing highlight the criticality of robust cybersecurity measures. The potential consequences of cyberattacks, including operational disruption, intellectual property compromise, safety risks, supply chain disruptions, and financial and reputational damage, underscore the need for a proactive and comprehensive approach to cybersecurity.
As we have explored the challenges associated with securing interconnected systems, supply chain vulnerabilities, remote access, the evolving threat landscape, and the importance of cybersecurity awareness, it becomes evident that industrial manufacturers must prioritize cybersecurity as a fundamental aspect of their operations.
So, without further ado, let’s learn about some essential cybersecurity best practices specifically tailored for industrial manufacturers.
Essential Cybersecurity Best Practices for Industrial Manufacturers
Effective cybersecurity measures are crucial for industrial manufacturers to protect their critical systems and data. Here are seven essential best practices that can significantly enhance cybersecurity in the industrial manufacturing sector:
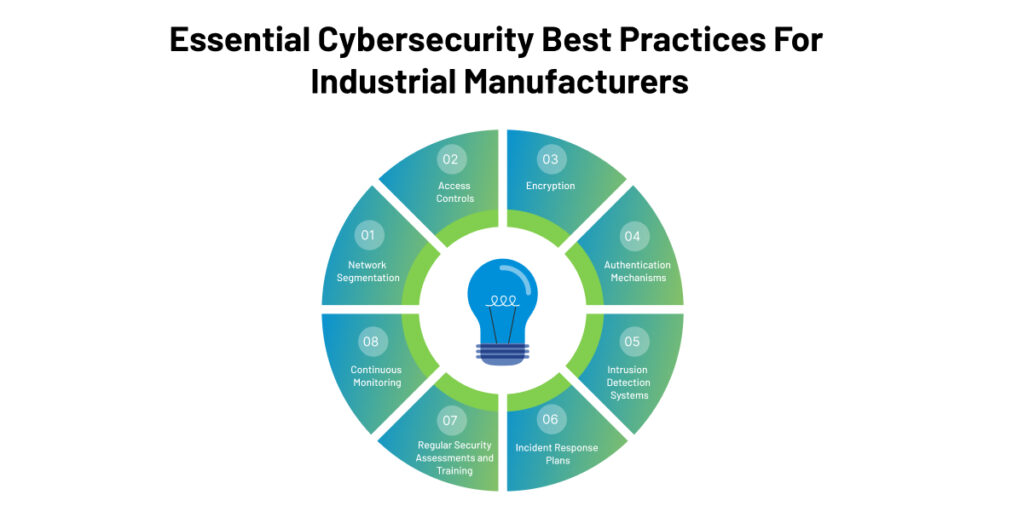
- Network Segmentation: Divide the network into separate segments to restrict unauthorized access and contain potential breaches. Segmentation helps prevent lateral movement by isolating critical systems and limiting the impact of an attack.
- Access Controls: Implement strong access controls to ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive systems and data. This includes using multi-factor authentication (MFA), strong passwords, and regular access reviews to prevent unauthorized access.
- Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data both at rest and in transit. Encryption provides an additional layer of protection, making it difficult for attackers to access or decipher the information, even if they gain unauthorized access to the systems.
- Authentication Mechanisms: Implement robust authentication mechanisms to verify the identity of users and devices accessing the network. This may include technologies such as digital certificates, biometric authentication, or secure tokens to enhance the security of the authentication process.
- Intrusion Detection Systems: Deploy intrusion detection systems (IDS) to monitor network traffic and detect suspicious or malicious activity. IDS can help identify potential cyber threats in real-time, allowing immediate response and mitigation.
- Incident Response Plans: Develop comprehensive incident response plans that outline the steps to be taken during a cybersecurity incident. These plans should include containment, investigation, mitigation, and recovery procedures to minimize an incident’s impact and restore operations quickly.
- Regular Security Assessments and Training: Conduct regular security assessments to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the systems and infrastructure. This may include penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and risk assessments to address potential threats proactively.
Provide ongoing cybersecurity training and awareness programs for all employees to educate them about common threats, best practices, and their role in maintaining a secure environment. This helps foster a culture of cybersecurity awareness throughout the organization. - Continuous Monitoring: Implement constant monitoring solutions to promptly detect and respond to security incidents. This includes monitoring network traffic, system logs, and security alerts to identify anomalous or suspicious activities that may indicate a potential cyber threat.
By implementing these best practices, industrial manufacturers can significantly enhance their cybersecurity defenses. Regular security assessments, employee training, awareness programs, and continuous monitoring are crucial elements of a robust cybersecurity strategy. Cybersecurity is an ongoing effort, and manufacturers must adapt to the evolving threat landscape to effectively protect their operations, assets, and reputation.
Also, Read – The Role of Cloud Computing in Modern Manufacturing
Compliance and Regulations: Enhancing Cybersecurity in Industrial Manufacturing
Compliance with industry standards and regulations plays a vital role in bolstering cybersecurity in the industrial manufacturing sector. Let us explore the significance of adhering to relevant standards and regulations and how they contribute to a resilient cybersecurity posture.
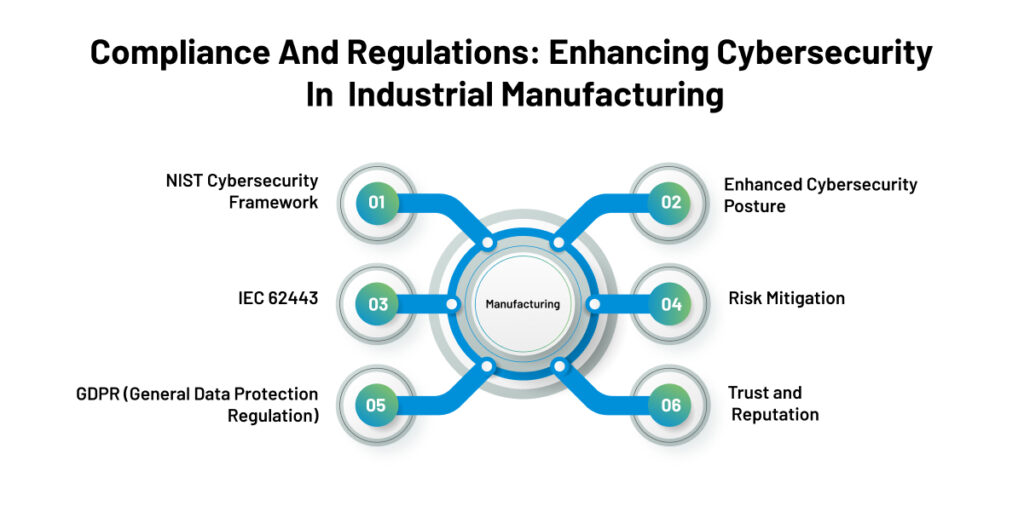
NIST Cybersecurity Framework: The NIST Cybersecurity Framework provides a comprehensive set of guidelines, best practices, and risk management approaches for organizations. Its implementation helps industrial manufacturers identify and prioritize cybersecurity risks, establish safeguards, and develop incident response capabilities. Adhering to this framework enables organizations to align their cybersecurity efforts with recognized industry standards.
IEC 62443: Specifically tailored for industrial automation and control systems (IACS), the IEC 62443 standard sets forth a comprehensive framework to address the unique cybersecurity challenges in the industrial manufacturing sector. Compliance with IEC 62443 ensures a systematic approach to securing IACS environments, including risk assessment, network segmentation, access control, and ongoing monitoring.
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): While GDPR primarily focuses on data privacy and protection, its implications for industrial manufacturers cannot be ignored. GDPR mandates stringent requirements for the handling and processing of personal data, including employee and customer information. Complying with GDPR helps organizations establish robust data protection practices, ensuring sensitive information’s confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Further, compliance with these standards and regulations offers several benefits to industrial manufacturers:
Enhanced Cybersecurity Posture: Compliance frameworks provide a structured approach to identify, assess, and mitigate cybersecurity risks. By adhering to these standards, organizations establish a solid foundation for a comprehensive cybersecurity program, addressing vulnerabilities and implementing appropriate safeguards.
Risk Mitigation: Compliance requirements often align with industry best practices, ensuring organizations implement robust security controls and measures. By following these guidelines, manufacturers can proactively identify and mitigate potential risks, reducing the likelihood of cyber incidents and their impact.
Trust and Reputation: Complying with industry standards and regulations demonstrates a commitment to cybersecurity and data protection. This builds trust among customers, partners, and stakeholders, enhancing the organization’s reputation and competitive advantage.
However, compliance alone is not enough. Industrial manufacturers must view compliance as a starting point and continuously strive for improvement. Regular assessments, audits, and monitoring of cybersecurity practices ensure ongoing compliance and adaptability to emerging threats.
Conclusion
As industrial manufacturing embraces digitization, the importance of cybersecurity cannot be overstated. The interconnectedness of systems, the reliance on critical infrastructure, and the growing sophistication of cyber threats present significant challenges for manufacturers. Safeguarding assets, ensuring production continuity, protecting sensitive data, and prioritizing the safety of employees and the environment are paramount in this era.
Cyber threats in industrial manufacturing can have devastating consequences, including operational disruptions, intellectual property compromise, safety, and environmental risks, supply chain disruptions, and financial/reputational damage. Robust security measures are crucial due to cyberattacks’ increasing frequency and sophistication.
Industrial manufacturers must adopt essential cybersecurity practices, including network segmentation, access controls, encryption, authentication mechanisms, intrusion detection, incident response plans, security assessments, training programs, and continuous monitoring.
Compliance with industry standards like NIST Cybersecurity Framework, IEC 62443, and GDPR enhances cybersecurity posture and mitigates risks. Following these frameworks provides a structured approach to identify, assess, and mitigate cybersecurity risks, fostering trust and demonstrating a commitment to data protection.
In this dynamic landscape, seeking guidance from IT transformation consulting firms can provide valuable expertise and insights. These consulting partners can assist in developing tailored cybersecurity strategies, implementing best practices, and navigating compliance requirements, empowering industrial manufacturers to stay ahead of evolving threats and secure their digital transformation journey.
By prioritizing cybersecurity and adopting proactive measures, industrial manufacturers can navigate the cybersecurity challenges of digitization, protect their assets and operations, and embrace the opportunities and benefits that the era of industrial manufacturing digitization brings.




