In the ever-evolving manufacturing landscape, the rise of industrial automation presents a compelling narrative of progress and innovation. As industries seek to stay competitive and resilient in an increasingly dynamic global market, the allure of automation becomes undeniable. It promises streamlined processes, heightened productivity, and optimized workflows, all while reducing operational costs and elevating the overall quality of products.
However, beneath this promising facade lies an intricate web of challenges that manufacturers must navigate to reap the actual benefits of automation. Technological complexities, integration hurdles, and the human element of the workforce pose formidable barriers that demand astute planning and insightful strategies.
At the heart of these challenges lies the quest to strike a harmonious balance between human ingenuity and the prowess of machines. Ensuring a seamless collaboration between human operators and automated systems requires thoughtful consideration of roles, responsibilities, and skill development.
Moreover, the digital transformation demanded by automation necessitates reevaluating existing processes, supply chains, and data management practices. Adapting to these changes may be daunting, but it is also a remarkable opportunity to drive organizational growth and adaptability.
This article embarks on an insightful journey into industrial automation implementation. We explore the complexities manufacturers face, analyze the strategies employed by visionary industry leaders, and seek to unravel the secrets behind successful integration.
As we traverse the landscape of intelligent manufacturing, we will find that process automation challenges are not insurmountable barriers but gateways to progress. By delving into the heart of these challenges and unearthing effective strategies, we fully equip ourselves with the knowledge and vision needed to embrace industrial automation’s transformative power.
So, let us delve deeper into understanding the essence of industrial automation, where human expertise meets cutting-edge technology and the potential for manufacturing excellence knows no bounds.
Also Read – Unlocking the Potential of Intelligent Automation: A Guide for Enterprises
Overview of Industrial Automation in Manufacturing
In recent years, automation technologies have become more advanced, accessible, and versatile, substantially impacting various manufacturing sectors. Today, process automation is not just a trend but a necessity for industries striving to stay competitive, agile, and efficient in a fast-paced global market.
Automation in manufacturing encompasses a wide range of technologies, including robotics, artificial intelligence, machine learning, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and data analytics. These technologies work harmoniously, creating a seamless network of interconnected systems that optimize production processes, enhance decision-making, and revolutionize manufacturing goods.
One of the most notable trends in industrial automation is the integration of collaborative robots or cobots. Unlike traditional industrial robots, cobots are designed to work alongside human operators, assisting with repetitive tasks and increasing productivity without compromising safety. This human-robot collaboration improves efficiency and enhances the work environment, empowering workers to focus on higher-value tasks requiring creativity and problem-solving skills.
Furthermore, artificial intelligence and machine learning have emerged as game-changers in industrial automation. These technologies enable machines to analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make real-time autonomous decisions. As a result, manufacturing processes can be optimized, predictive maintenance can be implemented, and production bottlenecks can be proactively addressed, leading to increased operational efficiency and reduced downtime.
Further, to better understand the significance of industrial automation in manufacturing, let’s look at its key benefits.
Key Benefits of Industrial Automation in Manufacturing:
Industrial automation in manufacturing offers a wide array of benefits, some of which are well-known, while others may not be as widely recognized. Here are some of them:
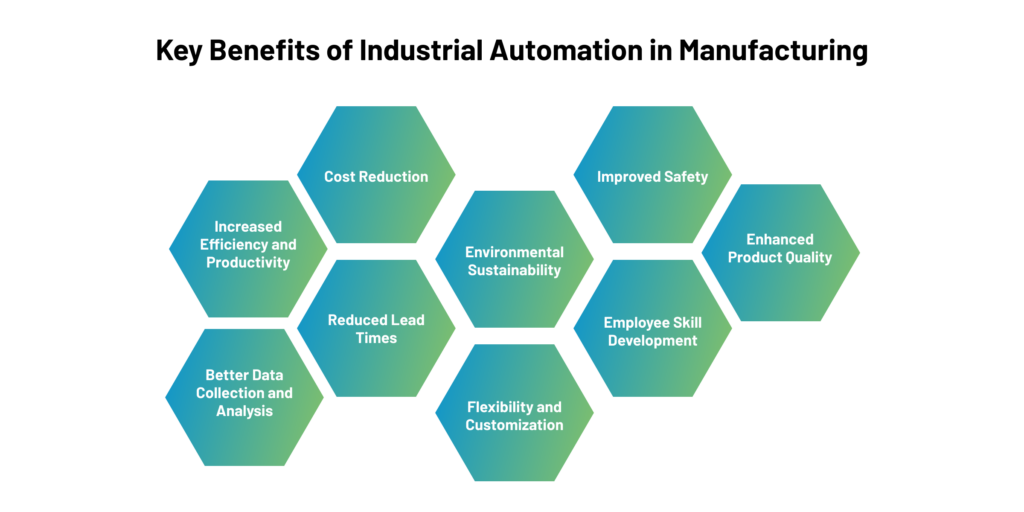
Increased Efficiency and Productivity: Automation streamlines manufacturing processes, reducing human errors and increasing production speed. This leads to higher productivity levels, improved cycle times, and efficiency gains.
Cost Reduction: Process Automation can lead to significant cost savings in the long run. Though the initial investment may be high, the reduced need for manual labor, minimized material waste, and optimized energy consumption lowers operational costs.
Enhanced Product Quality: Automated systems can consistently perform tasks with high precision and accuracy, ensuring uniform product quality. This consistency results in fewer defects and improved customer satisfaction.
Improved Safety: Repetitive and hazardous tasks can be assigned to automated machines, protecting workers from potential injuries. This not only enhances the safety of the workforce but also reduces insurance costs and associated liabilities.
Better Data Collection and Analysis: Automation facilitates real-time data monitoring and collection. Manufacturers can use this data to gain valuable insights into their processes, identify areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions to optimize performance.
Flexibility and Customization: Modern automation systems are designed to be adaptable to different manufacturing needs. They can be reprogrammed and reconfigured to produce various products, enabling faster transitions between production lines.
Reduced Lead Times: Automated processes can significantly reduce manufacturing lead times. Quicker production and assembly times mean products can reach the market faster, giving companies a competitive advantage.
Environmental Sustainability: Process automation can contribute to sustainability efforts by optimizing resource utilization, minimizing waste generation, and reducing energy consumption. This eco-friendly approach helps manufacturers to be more environmentally responsible.
Employee Skill Development: Contrary to the fear that automation may eliminate jobs, it often leads to a shift in job roles. Employees can be upskilled to operate and maintain automated systems, focusing on higher-value tasks that require problem-solving and creativity.
However, despite the remarkable progress in industrial automation, challenges persist. The transition to automation requires substantial investments in both technology and workforce upskilling. For a better understanding, let’s unveil the critical challenges of adopting industrial automation in manufacturing.
Also, Read – The Future of Supply Chain Management: Digitalization and Automation
Top Challenges of Implementing Industrial Automation in Manufacturing
Here are the top challenges of implementing industrial automation in manufacturing:
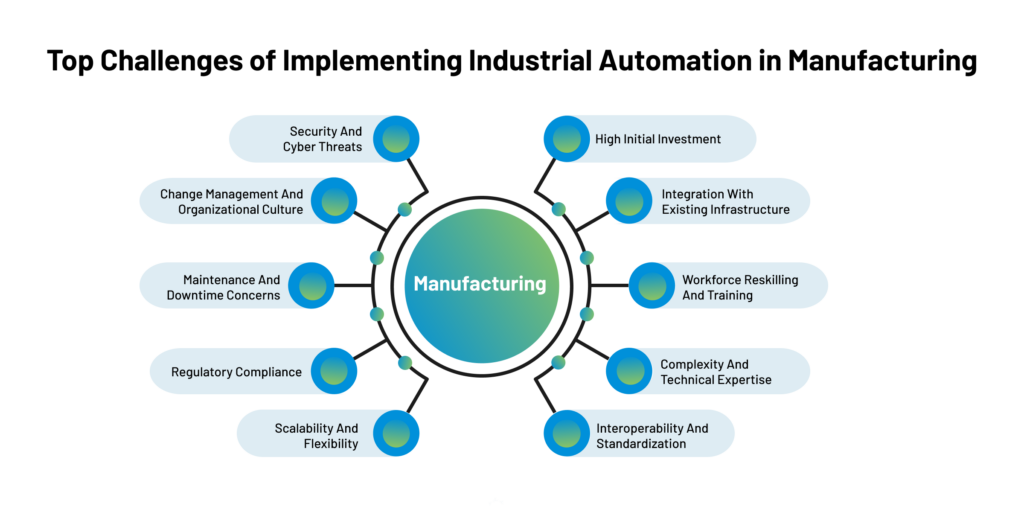
High Initial Investment: The substantial upfront cost is one of the most significant hurdles in adopting manufacturing automation. The required machinery, sensors, robotic systems, and software can be expensive, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Organizations must carefully analyze the return on investment (ROI) and long-term benefits to justify the initial capital expenditure.
Integration with Existing Infrastructure: Manufacturers often have legacy systems and equipment not designed with automation. Integrating new automated processes with existing infrastructure can be complex and require additional modifications or retrofits to ensure compatibility and smooth functioning.
Workforce Reskilling and Training: Automation can lead to changes in job roles and responsibilities. As tasks are automated, employees must acquire new skills to manage and maintain the automated systems effectively. Training the existing workforce or hiring new skilled personnel can be challenging and time-consuming.
Complexity and Technical Expertise: Automation systems can be intricate, involving advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and complex programming. Implementing and maintaining these systems requires a skilled technical workforce with robotics, software development, and data analytics expertise.
Interoperability and Standardization: Different automation technologies and equipment from various vendors may need to work seamlessly in a manufacturing environment. Lack of standardization can lead to compatibility issues and difficulties in creating a unified and efficient automation ecosystem.
Security and Cyber Threats: As manufacturing facilities become more connected through the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and automation, they also become susceptible to cyber threats. Safeguarding critical data and intellectual property and preventing unauthorized access becomes paramount, necessitating robust cybersecurity measures.
Change Management and Organizational Culture: Introducing automation can disrupt the existing work processes and create resistance among employees who fear job displacement or unfamiliarity with new technologies. A well-planned change management strategy and a positive organizational culture that promotes innovation and adaptation are essential to overcome these challenges.
Maintenance and Downtime Concerns: Automated systems require regular maintenance and updates to ensure optimal performance. Sudden breakdowns or downtime due to technical issues can severely impact production, making efficient maintenance procedures crucial.
Regulatory Compliance: In regulated industries, implementing automation may require adherence to specific standards and compliance with safety regulations. Ensuring the automated processes meet all legal and safety requirements can be demanding.
Scalability and Flexibility: Manufacturers must consider the future scalability of their automation systems to accommodate changes in production demands and technological advancements. Ensuring the automation setup remains flexible enough to adapt to evolving business needs is a constant challenge.
Addressing these challenges requires a well-thought-out strategy, collaboration between different departments within the organization, and a willingness to embrace technological advancements while considering the workforce’s well-being. With careful planning and execution, industrial automation can significantly enhance manufacturing processes and competitiveness. How? Let’s look.
Strategy to Overcome Challenges in Implementing Industrial Automation
To overcome the challenges of implementing industrial automation in manufacturing, organizations can follow a strategic approach that involves seven key steps. Each step addresses specific aspects of the challenges and aims to create a comprehensive and successful automation implementation plan:
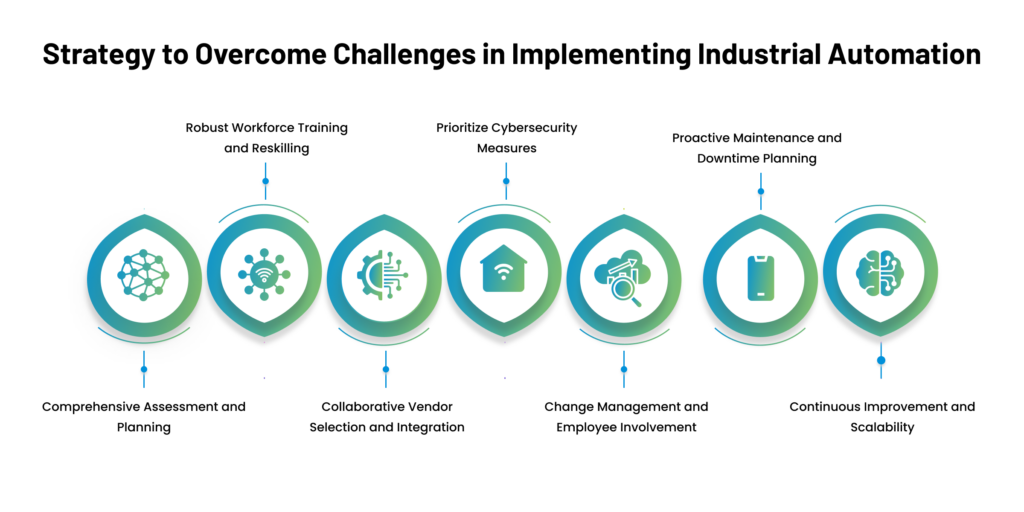
Comprehensive Assessment and Planning:
- Conduct a thorough analysis of the current manufacturing processes, infrastructure, and workforce capabilities. Identify the areas that can benefit most from automation.
- Set clear objectives and key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of the automation implementation.
- Develop a detailed roadmap for automation integration, including timelines, budget estimates, and resource requirements.
Robust Workforce Training and Reskilling:
- Identify the skills and knowledge gaps in the existing workforce concerning automation technologies.
- Design and implement training programs to equip employees with the skills to work alongside automated systems.
- Communicate the benefits of automation to employees and involve them in the process to reduce resistance and increase engagement.
Collaborative Vendor Selection and Integration:
- Choose automation vendors with a proven track record, standardized technologies, and a commitment to collaboration and support.
- Ensure that the selected automation solutions can integrate seamlessly with the existing infrastructure and each other.
- Establish strong communication channels between the organization and vendors to proactively address compatibility issues.
Prioritize Cybersecurity Measures:
- Develop a robust cybersecurity strategy that includes encryption, firewalls, access controls, and regular security audits.
- Train employees to recognize and respond to potential cyber threats, emphasizing the importance of data security and confidentiality.
- Implement regular updates and patches to software and hardware systems to address security vulnerabilities.
Change Management and Employee Involvement:
- Create a positive and transparent communication plan to inform employees about the benefits of automation and how it will impact their roles.
- Involve employees in planning and decision-making to give them a sense of ownership and reduce resistance to change.
- Celebrate early successes and recognize the efforts of employees adapting to the new automation systems.
Proactive Maintenance and Downtime Planning:
- Develop a proactive maintenance schedule for automated systems to minimize unplanned downtime and ensure optimal performance.
- Implement condition monitoring and predictive maintenance techniques to detect potential issues before they lead to significant problems.
- Have contingency plans to handle any unforeseen downtime or technical glitches to minimize disruptions to production.
Continuous Improvement and Scalability:
- Establish a culture of continuous improvement and innovation within the organization.
- Regularly review and update automation processes to adapt to changing business needs and technological advancements.
- Evaluate the success of the automation implementation using predefined KPIs and use the insights to refine the strategy for future scalability.
By following this comprehensive seven-step strategy, organizations can overcome the challenges of implementing industrial automation in manufacturing. This approach emphasizes the importance of people, technology, and processes working harmoniously to achieve successful automation integration and drive long-term benefits for the organization.
Wrapping it Up!
Manufacturing automation presents significant challenges and promising opportunities for organizations striving to stay competitive in an ever-evolving global landscape. Throughout this blog, we explored the significant hurdles companies may encounter when implementing automation and identified a seven-step strategy to overcome these obstacles.
Businesses can set the stage for a seamless transition to automation by conducting a thorough assessment and planning phase. Prioritizing the reskilling and training of the existing workforce ensures a more engaged and empowered workforce capable of leveraging the potential of automation to its fullest extent. Collaborative vendor selection and integration and a robust cybersecurity strategy safeguard the automation ecosystem from potential vulnerabilities.
Moreover, a strong emphasis on change management, involving employees in the decision-making process, fosters a positive and adaptable organizational culture that welcomes automation as a transformative force rather than a disruptive one. Proactive maintenance planning and downtime management guarantee the uninterrupted flow of production, maximizing the benefits of automation while minimizing potential risks.
As we move into the future, in addition to embracing future trends, organizations can further accelerate their journey toward successful industrial automation by partnering with digital transformation consulting firms. Partnering with a renowned digital transformation company can provide invaluable expertise and guidance, accelerating the successful implementation of automation and positioning businesses at the forefront of advanced manufacturing, ushering in a new era of smart, sustainable, and efficient manufacturing through industrial automation.




