The manufacturing industry has undergone significant transformations since the Industrial Revolution, fueled by the emergence of innovative technologies. However, the current and most remarkable shift is happening right now as we embrace Industry 4.0, signifying the fourth industrial revolution.
Industry 4.0 represents a comprehensive digital transformation within the manufacturing sector. Manufacturers harness the power of data, analytics, and artificial intelligence to optimize production processes, pioneer new business models, and create additional revenue streams. This revolution marks a momentous milestone, ushering in a new era of digitalization that profoundly impacts operations, production, and business models.
Businesses can gather and analyze data from every aspect of their operations by leveraging connected devices, sensors, and cloud computing. This empowers them to make data-driven decisions, increase efficiency, and minimize waste.
In this blog, we will delve deep into the evolution of Industry 4.0, tracing the manufacturing sector’s journey from automation to digital transformation. We will analyze the key drivers of Industry 4.0, explore the challenges and possibilities it presents for businesses, and provide insights on how organizations can prepare themselves for the future. But before we plunge into the intricacies of Industry 4.0, let’s first take a closer look at the previous Industrial Revolutions and their profound impact on the entire economy.
The Industrial Revolutions: A Journey Through Time and Transformation
Industrial revolutions have been crucial turning points in the history of manufacturing, and each has brought significant advancements and transformations.
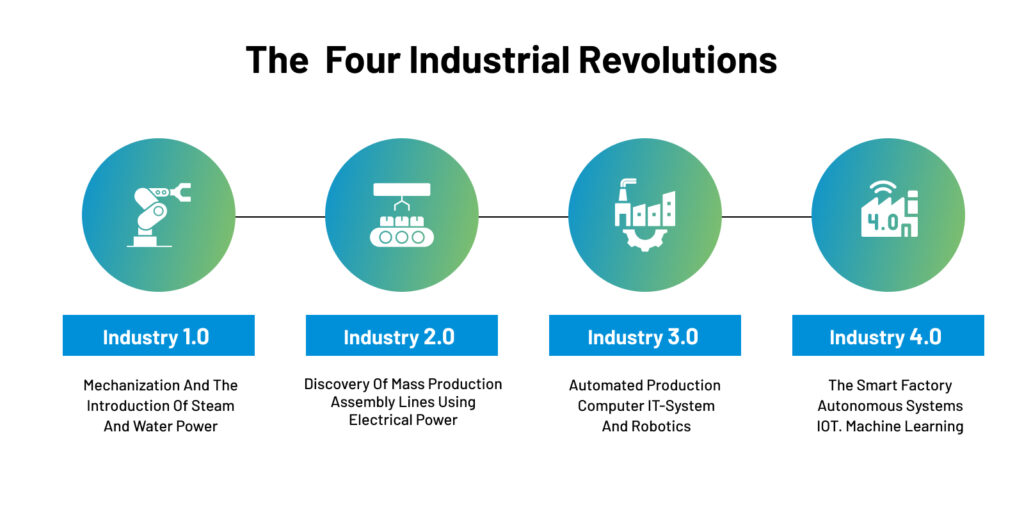
The first industrial revolution began in the late 18th century and marked the beginning of the mechanization of manufacturing. With the development of steam power, factories sprang up, and the textile industry was revolutionized. The transition from handmade goods to machine-made goods was a game-changer that boosted productivity and economic growth.
The second industrial revolution brought electricity and mass production to the manufacturing sector. Assembly line manufacturing and introducing new materials, such as steel, propelled manufacturing to new heights. It also saw the emergence of the automobile, which transformed transportation and opened up new business opportunities.
The Third Industrial Revolution, also known as the Digital Revolution, emerged in the late 20th century with the advent of computers, telecommunications, and the internet. It revolutionized manufacturing through automation, computerization, and integrating digital technologies into various industries. This led to improved efficiency, streamlined supply chains, and the rise of information technology.
And now come to the present – Fourth Industrial Revolution, or Industry 4.0. This ongoing revolution is marked by the fusion of digital, physical, and biological technologies. It includes advancements in artificial intelligence, robotics, the Internet of Things (IoT), 3D printing, biotechnology, and renewable energy. The Fourth Industrial Revolution is characterized by integrating cyber-physical systems and transforming industries such as healthcare, transportation, and manufacturing.
The industrial revolutions have brought us to where we are today, and the future looks bright. As we continue to embrace new technologies and push the boundaries of what is possible, we can expect even more innovation and transformation in the manufacturing industry. So, let’s buckle up and get ready to explore the most interesting industrial revolution – Industry 4.0.
Also, Read – Manufacturing Digital Transformation: What, How, and Why it Matters.
The Fourth Industrial Revolution: An Overview of Industry 4.0
Unlike previous revolutions that focused mainly on physical advancements in manufacturing, Industry 4.0 is centered on the digital transformation of the production process. It involves the seamless integration of physical systems with digital technologies, enabling self-optimization and communication.
At the heart of Industry 4.0 is digitization, which involves converting analog data into digital formats for easier processing, storage, and analysis. This allows manufacturers to collect and analyze data in real time, providing valuable insights to enhance efficiency, lower costs, and boost productivity.
Industry 4.0 is based on five fundamental components, each crucial to the system’s success. Let’s examine each component in detail:
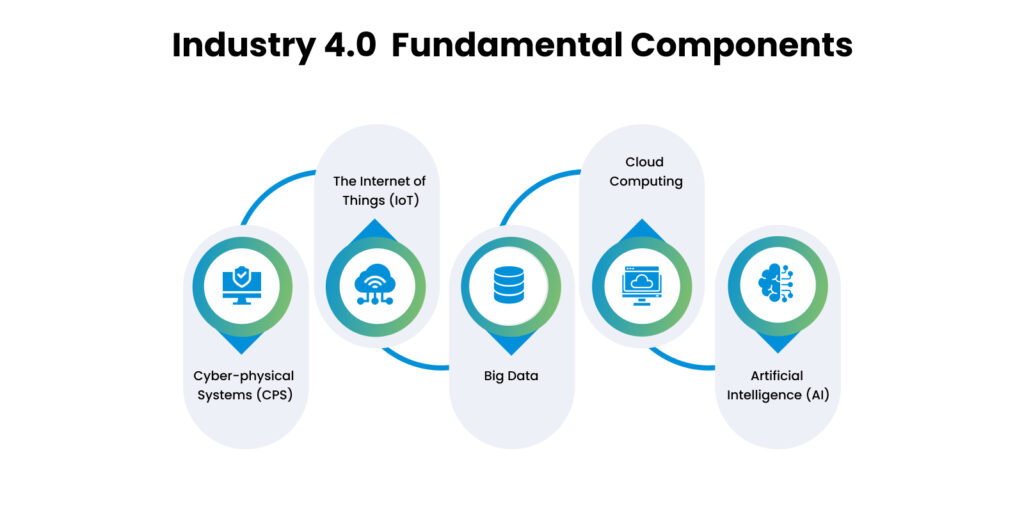
Cyber-physical Systems (CPS): CPS is the backbone of Industry 4.0. They are the integration of physical systems with digital systems, creating a network of interconnected devices and strategies that can communicate and optimize themselves. In addition, CPS enables manufacturers to monitor and control the production process in real time, making it possible to identify and address issues before they become critical.
The Internet of Things (IoT): The IoT is the network of physical devices, vehicles, and other objects embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity to enable them to exchange data. By connecting these devices, manufacturers can create a network of intelligent machines that can communicate and share information, allowing them to work together more efficiently and effectively.
Big Data: Big Data refers to the vast amounts of data generated by sensors, machines, and other digital systems in manufacturing. This data is analyzed to provide valuable insights into the production process, enabling manufacturers to optimize operations, reduce waste, and improve product quality.
Cloud Computing: Cloud computing allows manufacturers to store and process large amounts of data and access it anywhere. This allows for greater collaboration and real-time decision-making, enabling manufacturers to respond quickly to changing market demands and customer needs.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is the ability of machines to perform tasks that would typically require human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and language translation. AI enables manufacturers to automate repetitive and time-consuming tasks, allowing human workers to focus on more complex and creative tasks.
The impacts of Industry 4.0 are wide-ranging and significant. It increases industries’ efficiency, productivity, and sustainability, allowing for optimized resource utilization and reduced waste. It also leads to the creation of new business models and the disruption of traditional industries.
However, Industry 4.0 also presents challenges and considerations. It raises concerns about job displacement as automation replaces specific tasks previously performed by humans. Upskilling and reskilling the workforce to adapt to the changing technological landscape become crucial. Additionally, ethical considerations regarding data privacy, cybersecurity, and the responsible use of AI need to be addressed.
Overall, Industry 4.0 represents a transformative shift in how industries operate, leveraging advanced technologies to create smarter, more connected, and more efficient systems. It can potentially revolutionize various sectors and drive economic growth in the digital age.
The Role of Digitization in Industry 4.0
As read above, digitization is the driving force behind Industry 4.0, and its importance cannot be overstated. Industry 4.0 is using digital technologies to transform the manufacturing process, creating a more efficient, flexible, and connected system.
So let’s take a closer look at the vital role of digitization in Industry 4.0:
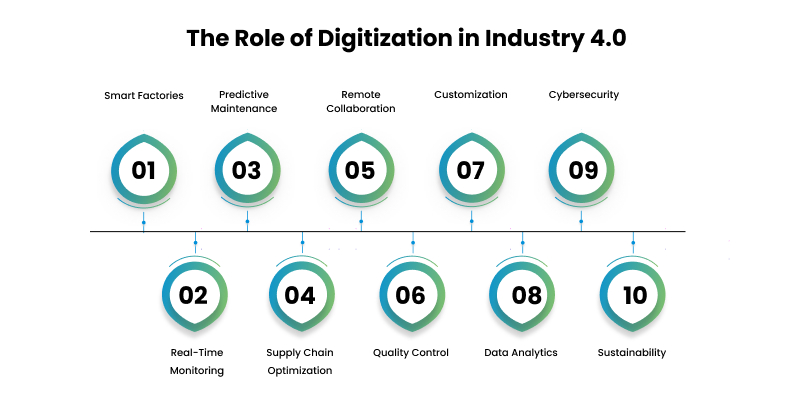
Smart Factories: Leveraging digitization, smart factories optimize manufacturing processes through interconnected machines, data analytics, and AI. These technologies automate tasks, reduce downtime, and enhance product quality. Sensors enable real-time monitoring, detecting issues in equipment before they escalate. Additionally, smart factories can adjust production processes based on changing demand or supply chain disruptions.
Real-time Monitoring: Real-time monitoring is made possible by digitization and involves using sensors and IoT devices. These devices collect and transmit data on equipment and processes to a central database, allowing businesses to monitor their operations in real-time. This data can be analyzed to identify patterns or potential issues and make informed decisions on optimizing processes or reducing costs.
Predictive Maintenance: Predictive maintenance uses data analytics and AI to predict when machines and equipment are likely to fail, allowing businesses to take preventive measures to avoid downtime. By collecting data on equipment usage, maintenance history, and other factors, predictive maintenance algorithms can identify patterns that indicate a machine is likely to fail. This approach helps to reduce maintenance costs and prolong the life of the equipment.
Supply Chain Optimization: Digitization enables supply chain optimization by providing real-time data on inventory levels, shipping times, and demand forecasts. This data can be used to make better decisions about when to order supplies or ramp up production. For example, businesses can reduce costs, improve efficiency, and respond quickly to changing customer needs by optimizing the supply chain.
Remote Collaboration: With digitization, teams can leverage digital tools and platforms to collaborate remotely. These tools facilitate the exchange of information and ideas, regardless of the team members’ location, thereby decreasing the requirement for physical presence in the office. Remote collaboration also permits organizations to provide flexible working arrangements, enhancing employees’ work-life balance.
Quality Control: The implementation of digitization in businesses can enhance the efficiency of quality control measures. It enables the collection and analysis of real-time data on product defects and deviations, facilitating prompt identification and correction of issues and reducing costs associated with product recalls or returns while improving customer satisfaction.
Customization: The personalization process can be facilitated by business digitization, which allows for customized products and services. Businesses can determine individual preferences and provide tailored offerings through customer data analysis, leading to higher customer loyalty and potential revenue growth.
Data Analytics: Sophisticated data analytics tools can be utilized to scrutinize the substantial quantities of data produced by digitization. These tools can reveal useful discernments into customer conduct, market patterns, and operational efficiency. Enterprises can enhance their performance and sustain competitiveness by employing these insights to make informed judgments.
Cybersecurity: With increased digitization comes an increased risk of cyber threats. Businesses must implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect their data and prevent cyber-attacks. These measures may include firewalls, encryption, and regular software updates to mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
Sustainability: By utilizing digital technology, businesses can decrease their environmental footprint through the optimization of energy usage and waste reduction. Real-time data can be used to monitor and assess energy consumption, thereby identifying potential areas for efficiency improvement and reduction of consumption.
Additionally, digitization has a crucial role in promoting sustainable manufacturing practices, which means businesses can adopt an environmentally conscious approach to their operations and manufacturing processes.
When it comes to Industry 4.0, businesses need to understand that digitization is crucial to stay competitive and thrive in today’s rapidly changing market.
However, it’s essential to acknowledge that challenges must also be addressed along with the benefits. But what are these challenges? Let’s have a look.
Also, Read – The Influence of Smart Factory on the Manufacturing Industry: A Closer Look.
Industry 4.0 Challenges
Implementing Industry 4.0 and embracing digitization come with their fair share of challenges. Let’s explore some of the key challenges businesses may face:

One major challenge is the potential displacement of human workers as advanced technologies are integrated into industries. This can lead to job losses and shift labor market dynamics. To address this, significant investments in retraining and upskilling programs are necessary to equip workers with the skills needed for the new industry landscape.
Another obstacle lies in the potential disruption of traditional supply chains. The use of advanced technologies in production may emphasize customization and flexibility, leading to the decentralization of manufacturing and the emergence of smaller supply chains. This can result in a redistribution of production and supply chain networks, with new production centers arising worldwide.
Cybersecurity is another critical challenge associated with Industry 4.0. The cyber-attack risk also rises as the use of connected devices and networks increases. Protecting data and systems from cyber threats is crucial to avoid significant economic and social repercussions.
Furthermore, adopting Industry 4.0 technologies can potentially exacerbate existing global economic inequalities. Countries and firms already advanced in their technological capabilities will likely reap the initial benefits, creating a potential gap between the technological “haves” and “have-nots.” This can impact both developed and developing economies, necessitating efforts to bridge this divide and ensure equitable access to the benefits of Industry 4.0.
Lastly, introducing Industry 4.0 requires shifting policies and regulations concerning data privacy, intellectual property, and trade. As advanced technologies become more integrated into production and supply chains, new regulations must be established to ensure their ethical and responsible use and the fair sharing of benefits across society.
Addressing these challenges requires a proactive and coordinated effort from governments, businesses, and civil society. In addition to investing in retraining and upskilling programs, there is a need to design policies and regulations that promote the ethical and responsible use of advanced technologies, ensuring that the benefits of Industry 4.0 are distributed fairly and equitably.
Strategies of Industry 4.0 Implementations
Define a Clear Vision: Start by creating a clear vision that outlines the organization’s objectives for Industry 4.0. This could involve improving productivity, reducing costs, increasing flexibility, or enhancing customer experiences. Communicate this vision effectively across the organization to ensure alignment and shared understanding.
Develop a Comprehensive Roadmap: Create a detailed roadmap that encompasses the adoption of critical technologies such as IoT, AI, and robotics. Consider the organization’s existing infrastructure, processes, and capabilities. Establish specific goals, milestones, and timelines to measure progress effectively.
Secure Stakeholder Buy-In: Gain support and buy-in from stakeholders at all levels, including executives, managers, and front-line workers. Engage stakeholders early in the process and effectively communicate the benefits of Industry 4.0. Address concerns and provide support and training to help stakeholders understand the impact of the changes.
Focus on People and Culture: Cultivate a culture prioritizing innovation and continuous improvement. Invest in employee training and development, equipping them with the skills needed for the evolving industry. Foster a culture that encourages experimentation, risk-taking, and continuous learning.
Collaborate with Technology Providers: Forge partnerships with a digital transformation consulting firm with a proven track record of proffering the best Industry 4.0 solutions to business leaders. Leverage their expertise, resources, and guidance to identify practical solutions and facilitate implementation. Seek ongoing support and maintenance from these partners.
Embrace Data-Driven Decision-Making: Emphasize data-driven decision-making by implementing systems for data collection, storage, analysis, and visualization. Utilize data to optimize operations, improve performance, identify areas for improvement, reduce costs, and uncover new growth opportunities.
Embracing the power of interconnected technologies, data-driven decision-making, and a culture of innovation, businesses can unlock new levels of efficiency, productivity, and growth. The journey towards Industry 4.0 may require careful planning and adaptation, but the rewards of increased competitiveness, improved customer experiences, and sustainable operations make it worthwhile.
Wrapping it Up!
In conclusion, the journey from automation to digital transformation represents the evolution of Industry 4.0, revolutionizing the way industries operate and paving the way for a new manufacturing era. From the early stages of automation and mechanization to the present-day advancements in interconnected systems, artificial intelligence, and data analytics, Industry 4.0 has reshaped the landscape of industrial processes.
Throughout this transformative journey, integrating digital technologies has brought numerous benefits to businesses, including increased efficiency, reduced costs, improved quality, and enhanced customer experiences. Automation has evolved into a holistic approach encompassing the Internet of Things (IoT), robotics, big data analytics, and cloud computing, enabling organizations to create smart factories and interconnected systems that optimize operations and drive innovation.
Digital transformation lies at the core of Industry 4.0, emphasizing the importance of embracing technological advancements and adopting a forward-thinking mindset. It requires businesses to redefine their strategies, restructure their operations, and upskill their workforce to thrive in a rapidly changing digital landscape. By leveraging Industry 4.0 technologies, organizations can unlock new opportunities, improve decision-making, and gain a competitive edge in the market.
However, along with these opportunities, challenges must be addressed. Upgrading infrastructure, ensuring data security, managing the influx of big data, and fostering a culture of innovation are some hurdles businesses face on the path to digital transformation. Overcoming these challenges requires a strategic and holistic approach involving collaboration with technology partners, investing in employee training, and staying abreast of technological advancements.
As we look toward the future, the potential of Industry 4.0 continues to expand. Advancements like edge computing, 5G connectivity, and advanced AI algorithms will further revolutionize industries and unlock new possibilities. The journey from automation to digital transformation is an ongoing process, and businesses that embrace this evolution will be well-positioned to succeed in the dynamic and competitive landscape of the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
So, what are you waiting for? Seek Industry 4.0 consulting with renowned experts like Copper Digital and pave the way for a successful digital transformation, unlocking the benefits of Industry 4.0.




