Industry 4.0, the fourth industrial revolution, is revolutionizing the manufacturing landscape. With the integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, robotics, quantum computing, and the Internet of Things, the very foundations of work are being reshaped. This paradigm shift towards automation and digitization has already begun, with manufacturing industries increasingly embracing these transformative technologies to streamline processes and optimize efficiency.
While the rise of Industry 4.0 brings immense potential for improved productivity and economic growth, it also presents unique challenges and considerations. Automating repetitive and mundane tasks previously performed by humans increases productivity and reduces human error. However, this shift necessitates reevaluating the workforce and their roles within this new framework. Upskilling and reskilling become crucial for employees to adapt to the changing demands of the digital age.
Additionally, the advent of Industry 4.0 requires a collaborative relationship between humans and machines. As machines take over routine tasks, humans can focus on more complex and creative endeavors that require critical thinking, problem-solving, and emotional intelligence. Nurturing these uniquely human skills becomes paramount to ensure that the workforce remains relevant and valuable in an automated environment.
In this blog, we’ll break down complex concepts into actionable insights, providing a roadmap for businesses to thrive amid technological disruption. Get ready to navigate the future of work in Industry 4.0 — where adaptability isn’t just a choice but a strategic imperative for success.
Also, Read – From Automation to Digital Transformation: The Evolution of Industry 4.0
The Impact of AI on Manufacturing Jobs
The impact of AI and automation on manufacturing jobs is significant and far-reaching. With the rapid advancement of AI technologies, the manufacturing industry is experiencing a transformation in how work is conducted. AI systems are increasingly capable of performing tasks traditionally carried out by humans, such as assembly line operations, quality control, and data analysis. This shift towards automation offers several advantages, including increased efficiency, improved productivity, and reduced human error.
However, adopting AI in manufacturing also raises concerns about potential job displacement. As machines take over specific roles, job losses are likely, mainly in repetitive and routine tasks. This necessitates a proactive approach to ensure that the workforce is prepared for the changes brought about by AI. Upskilling and reskilling programs become crucial to equip employees with the necessary knowledge and skills to adapt to new roles that require human creativity, problem-solving, and strategic thinking. Additionally, the collaboration between humans and AI systems becomes vital to leverage the strengths of both and create a symbiotic relationship that maximizes productivity and innovation in the manufacturing sector.
Further, as we delve into the impact of AI and automation on the manufacturing industry, it is essential to consider the implications for the future of work. By examining the prevailing trends and changes in the industry, we can gain insights into the evolving role of humans in manufacturing. Let’s explore these aspects further:
Trends in Industry 4.0
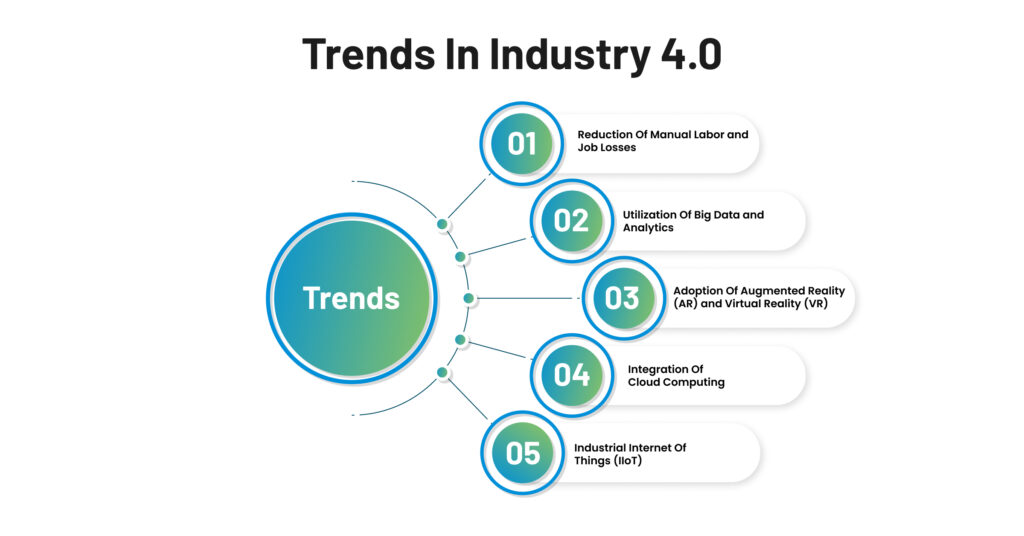
Reduction of Manual Labor and Job Losses
The emergence of AI in the manufacturing industry has increased efficiency and productivity. However, this progress has also resulted in a reduction in the demand for manual labor. In sectors like manufacturing, robots are increasingly replacing human workers, leading to job losses in certain areas.
Utilization of Big Data and Analytics
The manufacturing domain is witnessing a growing trend of utilizing big data and analytics. Manufacturers harness the power of large data sets to identify opportunities for enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and improving quality in real time. Smart sensors collect relevant data, then analyze using machine learning algorithms.
Adoption of Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
Industry 4.0 is paving the way for innovative technologies like AR and VR to enhance human-machine interaction. AR is widely used in manufacturing to provide workers with digital guides that assist in complex tasks, while VR is utilized for employee training.
Integration of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing enables Industry 4.0 by facilitating seamless data sharing across diverse platforms. Smart manufacturing leverages cloud computing to access the latest production-related software tools, fostering enhanced connectivity and collaboration.
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
The Industrial IoT has emerged as a critical trend in Industry 4.0. The IIoT enables companies to build intelligent and interconnected systems by integrating machine learning and AI algorithms. Network-connected devices gather and analyze data, leading to improved operational efficiency and the development of new business metrics.
Industry 4.0 has brought forth transformative technologies and trends reshaping the manufacturing landscape. While automation and AI-driven advancements are leading to increased efficiency and productivity, they also raise concerns about job losses due to the reduction of manual labor. However, it is essential to recognize that humans still play a vital role in the manufacturing industry within the context of Industry 4.0.
Despite the integration of robots and AI, human involvement remains crucial for various reasons. Let’s look at the reasons.
The Role of Humans in Manufacturing with Industry 4.0
In Industry 4.0, humans go beyond traditional roles, crucial in a tech-dominated landscape. AI, robots, and automation boost efficiency; humans contribute unique cognitive skills. Critical thinking, creativity, and adaptability are vital for handling complex tasks requiring human judgment. Humans continuously learn and adapt to evolving technology, effectively managing advanced machinery.
Moreover, humans excel in understanding context, empathy, and ethical considerations, bringing a nuanced perspective to manufacturing decisions. Their role extends to quality control, addressing issues, performing inspections, and making adjustments based on experience. Collaboration between humans and technology optimizes manufacturing operations in Industry 4.0.
AR and VR enhance human-machine interaction, providing intuitive guides and efficient training. In summary, humans are indispensable in the Industry 4.0 era. Cognitive abilities, adaptability, creativity, and ethical considerations contribute significantly to manufacturing success. Collaboration with advanced technologies is critical for efficient, sustainable, and responsible manufacturing.
However, Industry 4.0 poses challenges for jobs and employment. While automation boosts efficiency, concerns arise about job displacement and evolving work nature.
The Challenges of Jobs in Industry 4.0
The challenges of jobs in Industry 4.0 and the future of work can be summarized in the following points:

Automation and Job Displacement
The increasing use of automation, robotics, and AI technologies in Industry 4.0 can lead to job displacement as tasks traditionally performed by humans are automated. This can result in a shift in the job market and potential job losses in specific industries.
Skills Gap and Reskilling
Industry 4.0 demands a new set of skills and competencies that may not align with the skills possessed by the current workforce. There is a need for reskilling and upskilling programs to bridge the skills gap and prepare workers for the changing job requirements brought about by advanced technologies.
Structural Unemployment
The transformation of Industry 4.0 can lead to structural unemployment, where specific job roles become obsolete or significantly reduced in demand, creating challenges in workforce transition and reemployment.
Changing Job Roles and Responsibilities
With the integration of advanced technologies, job roles and responsibilities will undergo significant changes. Workers may need to adapt to new roles that require interaction with and management of technology and a higher level of digital literacy.
Unequal Access and Digital Divide
The adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies may be unevenly distributed, leading to unequal access to opportunities. The digital divide can exacerbate existing inequalities, creating challenges in ensuring an inclusive and equitable future of work.
Ethical Considerations and Job Design
As technologies become more advanced, ethical considerations surrounding job design and its impact on workers’ well-being become crucial. Ensuring that technology is designed and implemented to respect workers’ rights, health, and safety is a challenge that needs to be addressed.
Workforce Restructuring and Organizational Changes
Industry 4.0 significantly changes organizational structures, workflows, and business models. Companies may need to restructure and adapt their workforce to integrate and leverage advanced technologies effectively.
Continuous Learning and Lifelong Education
Technological advancements require workers to constantly learn and embrace lifelong education. The challenge lies in establishing systems and support for ongoing skill development and knowledge acquisition to keep up with evolving job requirements.
Overall, while Industry 4.0 presents numerous opportunities for increased productivity and efficiency, it also brings challenges related to job displacement, skills gaps, changing job roles, and ensuring a fair and inclusive future of work. Addressing these challenges requires proactive measures such as reskilling programs, digital inclusion initiatives, ethical considerations, and fostering a culture of continuous learning.
Also, Read – Industry-Specific Challenges in Manufacturing: How to Overcome Them
Strategies to Mitigate Job Challenges in Industry 4.0
Organizations and policymakers can implement several strategies to address the job challenges brought about by Industry 4.0. These strategies aim to mitigate the potential negative impacts of automation and technological advancements on employment while preparing the workforce for the changing job landscape. Here are some key strategies:

Reskilling and Upskilling Programs
Develop comprehensive initiatives to equip workers with the necessary skills and competencies for new job roles created by Industry 4.0. These programs should focus on digital literacy, data analytics, problem-solving, creativity, and adaptability.
Lifelong Learning Support
Establish a culture of lifelong learning by providing continuous learning opportunities for workers. Encourage employees to engage in professional development activities, online courses, and training programs to stay updated with emerging technologies and industry trends.
Collaboration between Academia and Industry
Foster closer cooperation between educational institutions and industry to align curriculum with the skill demands of Industry 4.0. This ensures graduates have relevant skills and knowledge, reducing the skills gap and promoting smoother workforce transitions.
Agile Workforce Planning
Implement agile workforce planning strategies that allow flexibility and adaptation to changing job requirements. Organizations should regularly assess their workforce needs, identify potential skills gaps, and develop proactive strategies to address them.
Job Redesign and Augmentation
Instead of focusing solely on job replacement, explore opportunities for job redesign and augmentation, where technology complements human workers rather than replacing them. Redefine job roles to leverage human capabilities that are difficult to automate, such as creativity, critical thinking, and emotional intelligence.
Social Safety Nets and Support Mechanisms
Implement social safety nets and support tools to assist workers affected by job displacement. This includes unemployment benefits, income support, retraining programs, and job placement services to facilitate smooth transitions and minimize the impact of job losses.
Ethical Considerations and Responsible Technology Deployment
Embed ethical considerations into the design and deployment of technology in the workplace. Ensure that technology is used responsibly, focusing on workers’ well-being, health, and safety. Implement guidelines and regulations that protect workers’ rights and prevent unethical practices.
Foster Collaboration and Communication
Encourage open communication between workers, unions, employers, and policymakers. This enables sharing of insights, concerns, and best practices to address the job challenges associated with Industry 4.0 collectively.
By adopting these strategies, organizations and policymakers can mitigate the potential negative impacts of job challenges in Industry 4.0 while ensuring that the workforce is adequately prepared for the changing nature of work.
Final Words
In the Industry 4.0 era, manufacturing faces promises and challenges due to advanced technologies like automation, AI, and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). These reshape the industry, boosting productivity. Still, it’s crucial to balance tech and human workers’ contributions amidst these changes.
Leaders must recognize humans and technology are complementary, not exclusive forces, for sustainable success. Implement reskilling and upskilling programs to equip workers with adaptable skills, fostering continuous improvement through lifelong learning initiatives.
Additionally, prioritize job redesign and augmentation to leverage human skills alongside technology. Redefine job roles to harness creativity, critical thinking, and emotional intelligence.
Moreover, industrial manufacturers must deploy technology ethically and consider workers’ well-being for a sustainable work environment. Balancing tech benefits with human dignity is crucial.
Collaboration between stakeholders is vital. By fostering a collaborative environment, diverse perspectives allow innovative solutions to emerge.
In conclusion, Industry 4.0’s future demands equilibrium between humans and technology. Recognizing unique strengths and implementing collaborative strategies ensures efficiency, innovation, and human-centered progress.
To navigate this balance, industrial leaders can benefit from digital transformation consulting firms, understanding digital complexities while preserving the human element for a harmonious and productive future.




